Variability
Variability
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) operates according to its own rhythms and is not controlled by us. The main functions of the ANS are the control of respiratory rate, heartrate, glandular secretion and the contraction and expansion of internal organs.The autonomic nervous system has two branches: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is activated when an individual is under pressure and anxious. When the stressful event is over, it is the turn of the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) to inhibit the activity, and return the body to a relaxed state. If there is an imbalance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves, a ” dysautonomia” occurs.
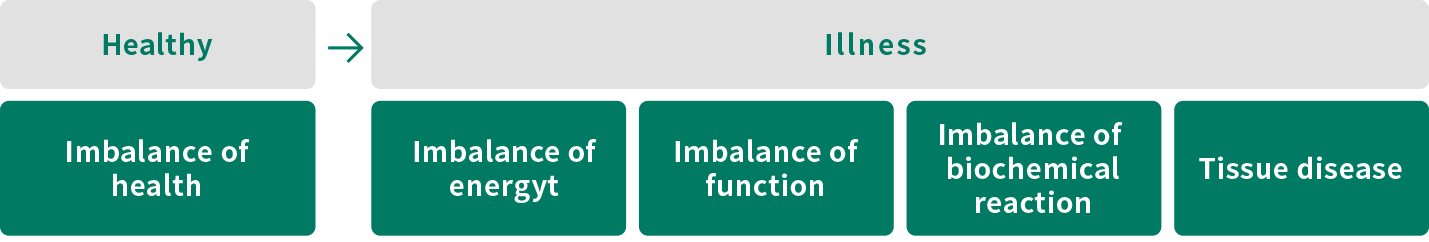
The term “dysautonomia” is not a single disease, but a group of symptoms. When the ANS becomes dysfunctional, the organs regulated by the ANS may begin to show symptoms. These symptoms are warning signs that the body is getting sick, because the body may still be functioning as normal and no obvious problems can be detected by a basic physical examination.
“Nervous exhaustion” is when the nerves are not supplied with enough energy, leading to symptoms such as lack of energy, low energy, and anxiety; “nervous hyperexcitability” is when the nerves are supplied with more energy than they can handle, leading to symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, and insomnia.
Reference:Diamond WJ (2000) The clinical practice of complementary, alternative, and Western medicine: CRC Press.

The autonomic nervous system (ANS) operates according to its own rhythms and is not controlled by us. The main functions of the ANS are the control of respiratory rate, heartrate, glandular secretion and the contraction and expansion of internal organs.The autonomic nervous system has two branches: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is activated when an individual is under pressure and anxious. When the stressful event is over, it is the turn of the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) to inhibit the activity, and return the body to a relaxed state. If there is an imbalance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves, a ” dysautonomia” occurs.
The term “dysautonomia” is not a single disease, but a group of symptoms. When the ANS becomes dysfunctional, the organs regulated by the ANS may begin to show symptoms. These symptoms are warning signs that the body is getting sick, because the body may still be functioning as normal and no obvious problems can be detected by a basic physical examination.
“Nervous exhaustion” is when the nerves are not supplied with enough energy, leading to symptoms such as lack of energy, low energy, and anxiety; “nervous hyperexcitability” is when the nerves are supplied with more energy than they can handle, leading to symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, and insomnia.
Reference:Diamond WJ (2000) The clinical practice of complementary, alternative, and Western medicine: CRC Press.
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) operates according to its own rhythms and is not controlled by us. The main functions of the ANS are the control of respiratory rate, heartrate, glandular secretion and the contraction and expansion of internal organs.The autonomic nervous system has two branches: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is activated when an individual is under pressure and anxious. When the stressful event is over, it is the turn of the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) to inhibit the activity, and return the body to a relaxed state. If there is an imbalance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves, a ” dysautonomia” occurs.
The term “dysautonomia” is not a single disease, but a group of symptoms. When the ANS becomes dysfunctional, the organs regulated by the ANS may begin to show symptoms. These symptoms are warning signs that the body is getting sick, because the body may still be functioning as normal and no obvious problems can be detected by a basic physical examination.
“Nervous exhaustion” is when the nerves are not supplied with enough energy, leading to symptoms such as lack of energy, low energy, and anxiety; “nervous hyperexcitability” is when the nerves are supplied with more energy than they can handle, leading to symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, and insomnia.
Reference:Diamond WJ (2000) The clinical practice of complementary, alternative, and Western medicine: CRC Press.



- The population who under pressure in working environments
- People who concerned about their physical and mental health states
- People with chronic physical and mental symptoms, such as insomnia, anxiety, mood disorders, etc.
- People with unhealthy lifestyles
- People with a family history of cardiovascular disease
- The population who under pressure in working environments
- People who concerned about their physical and mental health states
- People with chronic physical and mental symptoms, such as insomnia, anxiety, mood disorders, etc.
- People with unhealthy lifestyles
- People with a family history of cardiovascular disease
- The population who under pressure in working environments
- People who concerned about their physical and mental health states
- People with chronic physical and mental symptoms, such as insomnia, anxiety, mood disorders, etc.
- People with unhealthy lifestyles
- People with a family history of cardiovascular disease
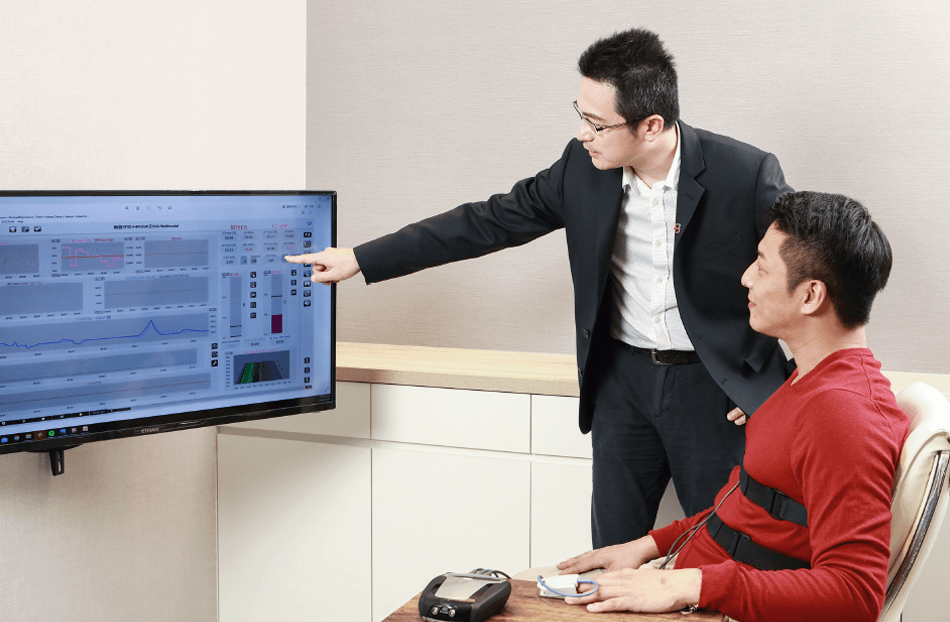
Exebrain uses “Heart Rate Variability (HRV)” to evaluate the function of the autonomic nerves and to determine the strength of the autonomic nerves by measuring the variation in the heartrate. People with autonomic nervous system disorders often have physical and psychological symptoms, but they have not yet been diagnosed with the disease; there usually seem to be no obvious illness of their health check results. However, the HRV test of Exebrain is scientifically quantified and easy to implement. The HRV test is non-invasive, high-accuracy and stable. Besides, Exebrain not only provides 5-minute procedure which conform to the internationally certified standards, but also 15-30 min HRV analysis.
Exebrain uses “Heart Rate Variability (HRV)” to evaluate the function of the autonomic nerves and to determine the strength of the autonomic nerves by measuring the variation in the heartrate. People with autonomic nervous system disorders often have physical and psychological symptoms, but they have not yet been diagnosed with the disease; there usually seem to be no obvious illness of their health check results. However, the HRV test of Exebrain is scientifically quantified and easy to implement. The HRV test is non-invasive, high-accuracy and stable. Besides, Exebrain not only provides 5-minute procedure which conform to the internationally certified standards, but also 15-30 min HRV analysis.
Exebrain uses “Heart Rate Variability (HRV)” to evaluate the function of the autonomic nerves and to determine the strength of the autonomic nerves by measuring the variation in the heartrate. People with autonomic nervous system disorders often have physical and psychological symptoms, but they have not yet been diagnosed with the disease; there usually seem to be no obvious illness of their health check results. However, the HRV test of Exebrain is scientifically quantified and easy to implement. The HRV test is non-invasive, high-accuracy and stable. Besides, Exebrain not only provides 5-minute procedure which conform to the internationally certified standards, but also 15-30 min HRV analysis.
The test is for medical professionals as a reference only. The clinical meaning of the test and related medical issues should be consulted with your physician.
The test is for medical professionals as a reference only. The clinical meaning of the test and related medical issues should be consulted with your physician.
The test is for medical professionals as a reference only. The clinical meaning of the test and related medical issues should be consulted with your physician.
